This is an old revision of the document!
LDAP and Role Based Access (RBA)
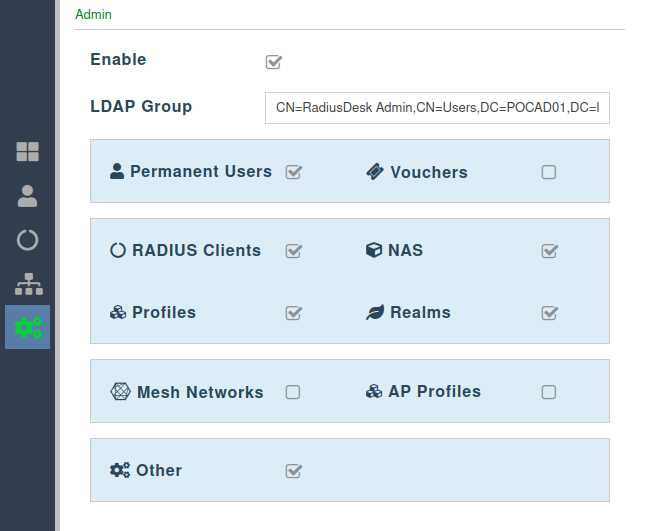
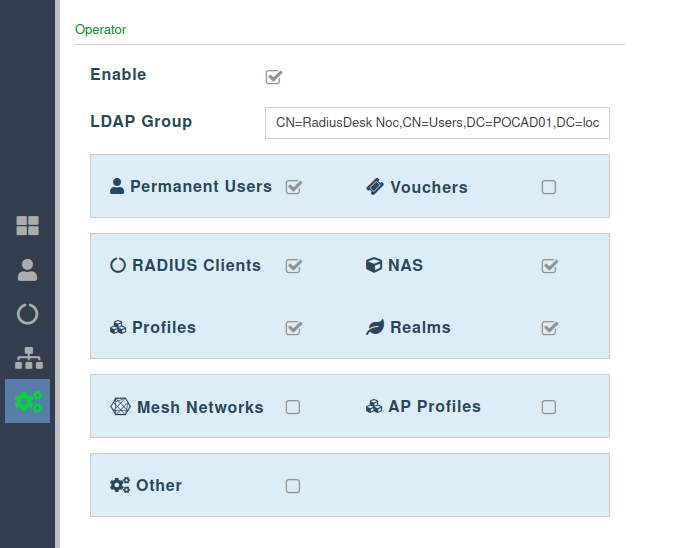
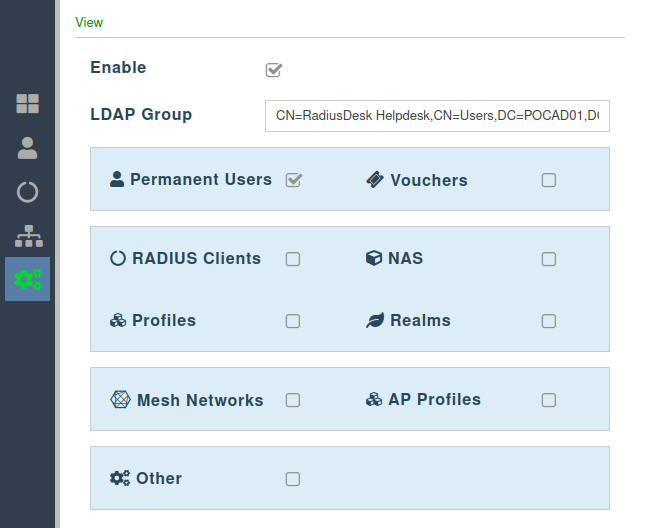
- RADIUSdesk allows the admin of a cloud to be in one of three possible roles.
- Admin
- Operator
- View
- The rights of the admin is dictated by the role they are in.
- This document will cover the optional configuration that allows you to map LDAP groups to the respective available roles.
Group Attribute
- The RADIUSdesk implementation allows you to specify the LDAP attribute which contains the groups a user belongs to.
- If you have an OpenLDAP deployment, you might have to add the memberof overlay.
- This link describes the process in more detail: https://tylersguides.com/guides/openldap-memberof-overlay/
- If you have an Active Directory deployment, make sure the user that does the initial bind can read the memberOf attribute.
- This link covers the items you need to double check: http://www.michaelm.info/blog/?p=1435
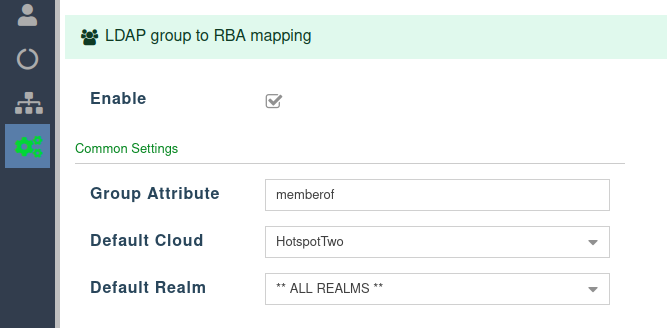
LDAP group to RBA mapping
Common Settings
- The LDAP group to RBA mapping is optional functionality available as a complement to the standard LDAP integration.
- To ensure that the LDAP user has a pleasant experience the first time they log in, we pre-define the default Cloud and Realm they will be assigned to.
- As stated earlier, we also give the option to specify the attribute that will contain the groups the user belongs to.
- The recommended value is memberof, all in lowercase.
Admin
- Client connects: The LDAP client (e.g., a user authentication script) connects to the LDAP server.
- Bind request: The client sends a bind request to the server, which includes the username (or DN) and password.
- Server authenticates: The server checks the username and password against its stored credentials.
- Bind response: If the credentials are valid, the server responds with a bind response, indicating a successful connection.
Operator
- Client connects: The LDAP client (e.g., a user authentication script) connects to the LDAP server.
- Bind request: The client sends a bind request to the server, which includes the username (or DN) and password.
- Server authenticates: The server checks the username and password against its stored credentials.
- Bind response: If the credentials are valid, the server responds with a bind response, indicating a successful connection.
View
- Client connects: The LDAP client (e.g., a user authentication script) connects to the LDAP server.
- Bind request: The client sends a bind request to the server, which includes the username (or DN) and password.
- Server authenticates: The server checks the username and password against its stored credentials.
- Bind response: If the credentials are valid, the server responds with a bind response, indicating a successful connection.